Kea 3.0, our first LTS version
ISC is excited to announce the release of Kea 3.0.0! This is a major release, and is the first Long-Term Support (LTS) version of Kea.
ReadCentralize monitoring and configuration
When your DHCP system isn’t configured correctly, or you have reachability problems, or a server has failed, it is an urgent problem. It is critical to find out and restore service quickly before other network services, that rely on DHCP, start failing. Stork can enable you to monitor a multi-server DHCP system quickly, making changes in status obvious and easy to spot.
Stork provides a web-based graphical interface for monitoring, troubleshooting, and maintaining the configuration of, Kea DHCP servers. Stork provides a single point for administrative control for your Kea servers, including integration with LDAP for administrator authentication and authorization. The graphical interface makes it possible for network administrators to easily make configuration updates to the DHCP service without having to struggle with unfamiliar CLI.
Stork is in the early stages of adding support for DNS, starting with BIND and read-only access to zone information.
Stork is open source, shared under MPL2.0 licensing. Stork is developed in the open on ISC’s GitLab; we welcome you to open issues and submit patches there. Stork runs on most Linux and Unix platforms, as well as MacOS. If you don’t want to build from our source distribution, we also provide a repository of pre-built packages for most popular operating systems, for both Kea and Stork.
Stork is comprised of two primary components: the Stork server (stork-server) and the Stork agent (stork-agent). Stork interacts with the Kea and BIND servers via the agents, installed on each application server. One Stork server is deployed in a network, providing an integrated, centralized front end for these services. The Stork server requires a PostgreSQL database, ideally installed on the same machine. The Stork server communicates with the agents via GRPC channels secured with TLS encryption. The Kea servers may also be using back end databases: Stork communicates with the Kea daemons and the daemons will manage any communications with their dependant databases. Stork can integrate with Prometheus and Grafana for warehousing and visualizing DHCP and DNS usage data. This is extremely useful for viewing trends over time, and for filtering and analyzing large amounts of traffic data.
Stork leverages several of the optional Kea hook libraries. We strongly recommend Stork users install at least the lease_cmds and stat_cmds on Kea servers they want to manage with Stork. Kea may optionally be deployed with a database backend for host reservations, and if it is, Stork will manage the host reservations in the database. Most Kea users deploy the optional high availability hook - if your Kea servers are configured to work as HA pair then Stork will use this library to display the HA status.
Stork requires the subnet_cmds hook installed on the Kea servers in order to modify subnets and pools: it also enhances the metrics passed to Prometheus by including subnet labels. Without this hook, Prometheus identifies subnets by subnet IDs. The subnet_cmds hook is commercially licensed for Kea versions prior to 2.7.7, and is open source with Kea 2.7.7 and later versions.
Stork does not require nor integrate with the optional Kea configuration backend at this time. The Configuration Backend hook cannot be used when managing Kea with Stork.
Stork requires the Stork agent for BIND, and access to the BIND systems via RNDC and AXFR, to obtain statistics and transfer zones for viewing. At this time Stork is reading and displaying, but not modifying any information in BIND.
On-line DEMO
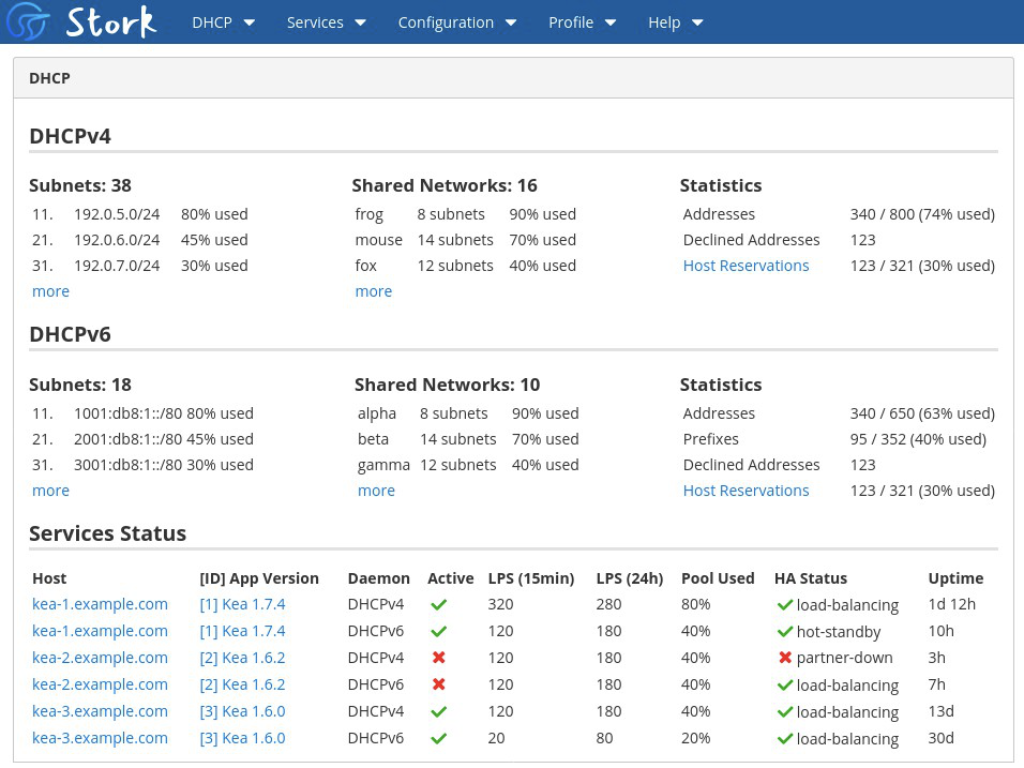
Stork aggregates data about the health of the systems, as well as the status and activity level of Kea and BIND daemons. Parameters reported include memory, CPU utilization, software versions, and uptime.
Stork displays configured pools, with # of addresses provisioned and assigned and even tracks pool utilization across shared networks. Graphical elements highlight areas of high utilization to alert the operator to take action. High Availability pairs are monitored and their configured role and status are shown, making it easy to see which servers don’t have a backup established, and when a failover event has occurred.
Add, update and view DHCPv4 and DHCPv6 host reservations, using a graphical interface to select a host identifier, assign a hostname, reserve an IP address, associate a client class, and configure boot file information and DHCP options. Add and modify subnet configurations in Kea using the Subnet Commands hook.
View a list of DNS zones, with associated servers and views. Fetch zone contents and compare serials between the same zone on different machines.
Your major design decisions are about how you plan to authenticate Stork users, and which of the Kea hooks to install. Stork leverages the Kea Host Commands hook for managing host reservations in Kea, and the Kea Subnet Commands hook for managing subnets in Kea and the Leases hook for querying Kea servers about leases.
There is a handy Quickstart Guide for installing Stork. ISC provides pre-built packages for RHEL, Fedora, Ubuntu, and Debian. If you are using any Kea hook libraries, you will also need to install and configure those.
The Stork Administrator Reference Manual (ARM) is the primary reference for Stork installation and use.
Most users will benefit from joining the stork-users mailing list. Consider joining our Stork project GitLab to log issues, see what we’re working on, submit patches, and participate in development. You might want to read about our Kea hook libraries, which Stork uses for management. If your DHCP is critical to your business, we recommend you subscribe for technical support from ISC.
Join the stork-users mailing list to offer help to or receive advice from other users.
Join NowBefore submitting a bug report please ensure that you are running a current version. Then log your report as an issue in our Stork GitLab project.
ReportPremium libraries add the Host Reservation API, Flexible Host Identifier, & Forensic Logging.
Buy